Compounding Pharmacy
Compounding is the art and science of creating customized medications tailored to individual patient needs. This practice has deep historical roots, dating back to the origins of pharmacy in ancient civilizations. Historically, pharmacists manually prepared most medications, creating personalized treatments for patients. While the advent of mass-produced pharmaceuticals in the 20th century shifted the focus away from compounding, the practice has seen a resurgence in recent years.
What Is Compounding
Personalized medicine is an approach to healthcare that involves using genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors to predict an individual’s risk of disease, to identify the best treatment options, and to develop a personalized treatment plan that considers each patient’s unique needs.
Compounding is an essential tool in the field of personalized medicine. Compounding pharmacists can create customized medications tailored to the individual needs of each patient based on factors such as dosage, route of administration, and specific ingredient preferences or allergies.
For example, a patient may require a medication in a specific dosage that is not commercially available or a drug in a particular dosage form, such as a cream or gel. Compounding pharmacists can prepare these medications in a customized formula tailored to the patient’s individual needs.
Compounding is an essential tool in the field of personalized medicine. Compounding pharmacists can create customized medications tailored to the individual needs of each patient based on factors such as dosage, route of administration, and specific ingredient preferences or allergies.
For example, a patient may require a medication in a specific dosage that is not commercially available or a drug in a particular dosage form, such as a cream or gel. Compounding pharmacists can prepare these medications in a customized formula tailored to the patient’s individual needs.

Benefits Of Compounding
Compounding also allows for the creation of medications that are free from potential allergens, dyes, or other additives that may be harmful or cause adverse reactions for certain patients. Compounding pharmacists can work with healthcare providers to develop a medication plan that takes into account the unique needs of each patient, including their medical history.
Types of Compounding
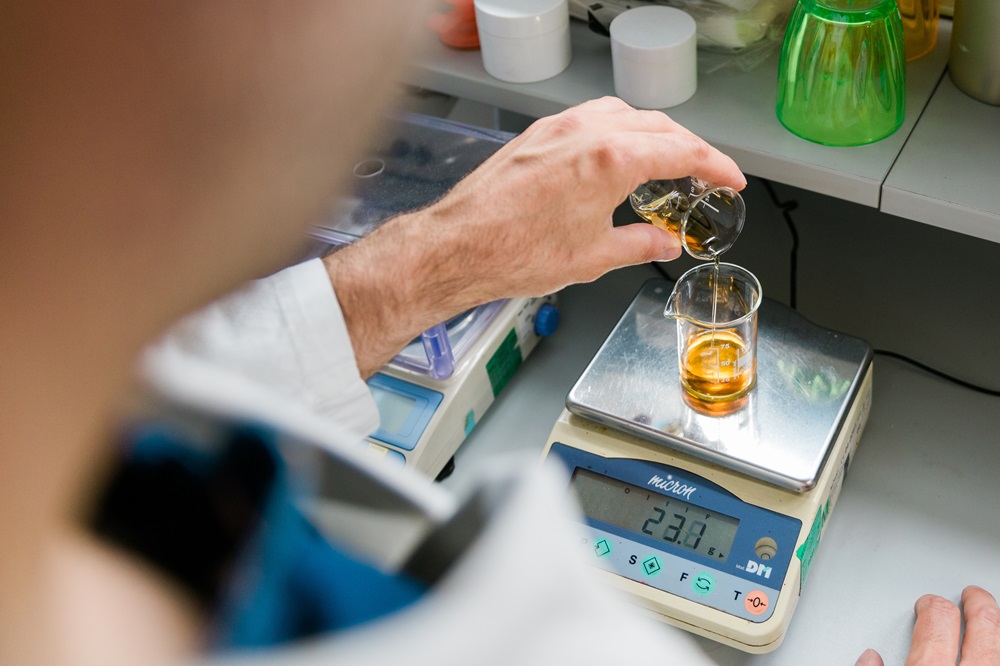
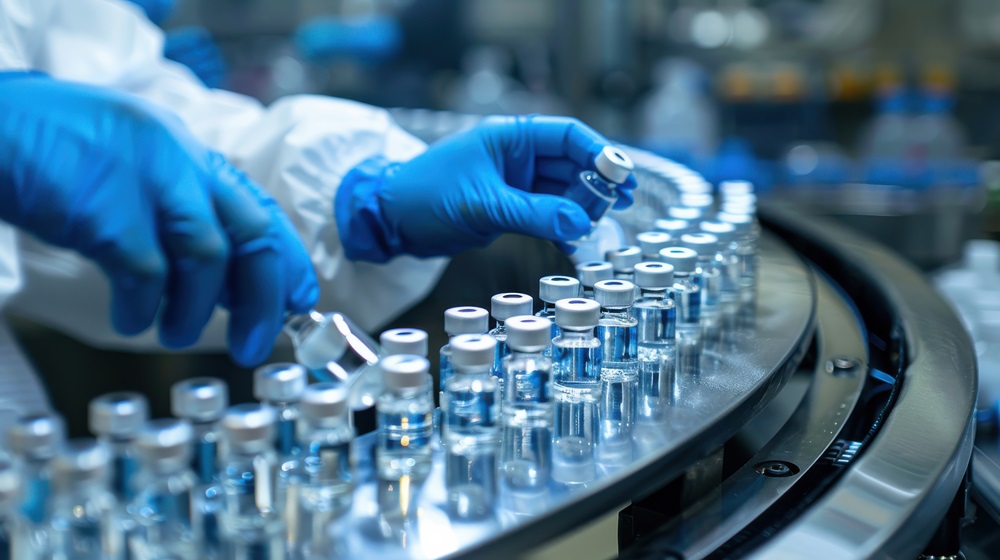
Sterile Compounding
Sterile compounding involves creating sterile medications specifically for injectable use. This process must be carried out in a meticulously controlled environment with precise procedures and specialized equipment to guarantee the safety and effectiveness of the final product.
Non-Sterile Compounding
Non-sterile compounding involves preparing medications in a non-sterile environment, typically for oral, topical, or other non-injectable applications. This process includes mixing, diluting, and manipulating raw materials to create customized medications tailored to patients’ needs.
Types Of Sterile Compounding
- Intravenous Solutions: Administered directly into the bloodstream for immediate and effective results.
- Intramuscular Solutions: Injected into muscle tissue for a gradual and sustained release.
- Subcutaneous Solutions: Delivered under the skin for slower, localized effects.
- Intracavernosal Injections: Precisely targeted injections for specific needs

Process of Sterile Compounding
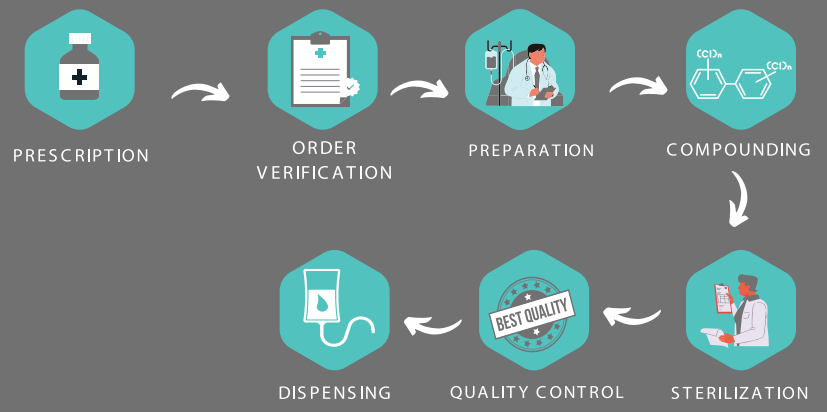
Types of Non-Sterile Compounding
- Capsules: Custom doses of medication in capsule form for patients needing specific strengths.
- Oral Suspensions: Liquid where medication is suspended for easier consumption and better taste.
- Lozenges/Troches: Dissolving tablets in the mouth for localized or slow-release effects.
- Creams/Ointments: Topical applications for skin conditions or localized treatment, with ointments being thicker.
- Gels: Clear preparations used for transdermal or topical treatments, often for hormones or pain relief.
- Lotions: Liquid for larger areas of the skin, usually for moisturizing or treating skin issues.
- Transdermal Patches: Skin patches that deliver medication slowly over time.
Process of Non-Sterile Compounding
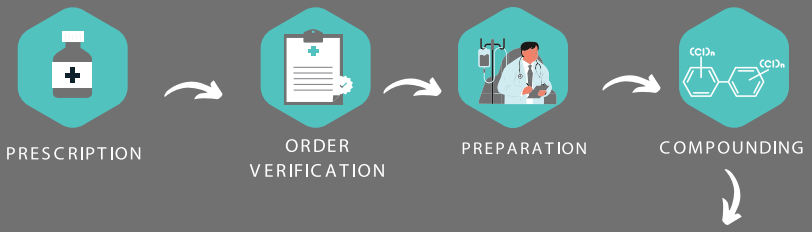

At CureCell, both sterile and non-sterile compounding are conducted in controlled environments using advanced equipment and strict procedures to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of every product, with each step performed meticulously to prioritize patient well-being.